What Is Porn Addiction: The Brain's Imbalance Between 'Wanting' and 'Liking'
Porn addiction is a state of craving when you don't have it, but not enjoying it as much when you do
1. You intensely "want" to watch porn, but don't "like" it as much
The first characteristic of porn addiction: You often have an urge to watch porn, but when you actually see pornographic content, you find it uninteresting.
Let's first consider a question: When someone watches erotic content for longer periods, more frequently, and for extended durations, does it mean they "like" watching this content and can derive pleasure from it? Logically, if a person obsessively does something day and night, it must be because they "like" it and it brings them happiness. As the saying goes, what you can endlessly invest in reveals where your talent and passion lie. Unfortunately, this doesn't hold true when someone is addicted to something, especially porn. In fact, the more time and energy invested, the less pleasure they feel. Moreover, as porn addiction deepens, this investment of time and energy transforms from a voluntary action into compulsive behavior. In other words, when someone is addicted to porn, they exhibit a state of intensely "wanting" but not "liking" it as much.
To explain why this state occurs, we first need to clarify what constitutes "wanting" and what constitutes "liking". Firstly, "wanting" here isn't the usual sense of wanting, like wanting to become a billionaire, get a promotion at work, or become popular at school. These are normal desires and states, and it's precisely because of this normal wanting that people continually strive. However, the definition of "wanting" in this article actually refers to a sense of urgency and immediacy. When you absolutely can't wait for something, you just want it immediately, and you become anxious, angry, or frantic if you don't get it - this state corresponds to the "wanting" described in this article. For example, the state you were in as a child when you eagerly unwrapped a birthday gift is "wanting". In the context of porn addiction, "wanting" refers to a state where all your thoughts are consumed by desire before obtaining it. You feel your life is miserable without pornographic content, and you're willing to do anything to watch porn - this state is "wanting".
So what is "liking"? "Liking" is the happiness and joy you feel after obtaining something, the smile that appears on your face. For instance, the sense of happiness you feel when eating a delicious dessert, or the excitement and joy after winning a competition - this is "liking". So the "liking" discussed in this article is what people normally understand as liking.
What does a state of intensely "wanting" but not "liking" as much look like? You can observe this in TikTok addicts. They keep scrolling through one video after another, but only stay on each video for a few seconds before immediately scrolling again. This repetitive, mechanical behavior continues late into the night until they're exhausted and finally realize it's time to sleep. They don't derive much pleasure from the short videos, but they can't help but keep scrolling - this is intensely "wanting" but not "liking" as much. In porn addiction, there's a behavior that similarly reveals that they don't enjoy or like the content they're currently browsing. This behavior is constantly "fast-forwarding" to what they think are interesting parts. But when they actually fast-forward to the corresponding content, they're unable to immerse themselves and enjoy it again, so they want to fast-forward again. They don't actually enjoy watching porn; they're just satisfying their "wanting". Real "liking" is when you're content with what you're currently browsing, you're completely immersed in it, there's no fast-forwarding or speed adjustment, you just want to appreciate it frame by frame like a beautiful movie.
According to scientific research, this mechanism of "wanting" more than "liking" is an innate mechanism in the human brain, existing in all normal people. However, in the brains of porn addicts, a severe imbalance has occurred. Look at the image below. The thick black-gray arrows and areas represent the robust neural circuits controlling the "wanting" desire in the brain, while the thin white lines and circled areas represent the fragile, restricted brain circuits controlling "liking" in the general population.
In other words, the circuits controlling "wanting" in the human brain are far more robust than those controlling "liking". How extreme can this strong-weak contrast be? In the human brain's nucleus accumbens (a group of neurons located between the basal ganglia and limbic system, playing an important role in the brain's pleasure center and capable of responding to stimuli such as food, sex, and drugs), the volume of the part controlling "liking" is only about one cubic centimeter, accounting for just 10% of the nucleus accumbens. This means the remaining 90% is controlling "wanting". This dramatic contrast also explains why so many people, after successfully pursuing a goal, don't feel much happiness for long and quickly become empty again. This is the brain mechanism - the human brain is set to constantly pursue certain goals, feeling painful when not achieved and empty soon after achieving them.
What chemical substances in these two different neural circuits in the brain transmit the feelings of "wanting" and "liking"? The concentration of dopamine controls the intensity of the "wanting" feeling, while substances corresponding to "liking" include endorphins, serotonin, oxytocin, endocannabinoids, and a series of other substances. To help you understand and remember, let me use a simple analogy. There are two roads in your brain, one controlling your "wanting" of things, the other controlling your "liking" of things. The road controlling "wanting" is wide and sturdy, while the road controlling "liking" is not only narrow but also prone to depressions. These two roads have different messengers. Dopamine is the messenger on the "wanting" road, constantly transmitting urgent commands to the brain, making people anxious and expectant. Substances like endorphins are the messengers on the "liking" road, constantly transmitting the message "it's not a big deal, enjoy life" to the brain. Although there are many types of messengers transmitting information on the "liking" road, they can't compete with the wide and broad "wanting" road, where countless dopamine messengers are galloping. So most of the time, the brain is in a state controlled by desire, unable to enjoy the present.
In other words, the situation where "wanting" far exceeds "liking" is actually somewhat manifested in ordinary people's brains, and is further amplified in the brains of porn addicts. You can also see from the right side of the above image that as time progresses, porn addicts' "liking" gradually decreases, but the usage dose and the desire to "want" gradually increase. This phenomenon is called the incentive-sensitization theory. What does this mean? When a person becomes addicted to porn, they become increasingly sensitive to all information and cues that make them addicted to porn, and increasingly "want" it. It's important to emphasize here that they don't become more sensitive to porn itself, but to cues and information related to porn. For example, when seeing an image, they immediately associate it with similar pornographic content. This sensitivity develops into associating any words or phrases they see with porn, causing the brain to start secreting dopamine frantically, producing an extreme desire to "want". However, when they actually see pornographic content, due to having seen so much, they've already developed tolerance and can't feel much pleasure.
2. Becoming extremely sensitive to porn cues, but developing tolerance to pornographic content itself
When you're addicted to porn, you start associating unrelated things with porn. You become extremely sensitive to cues that can trigger porn associations, while losing interest in actual pornographic content
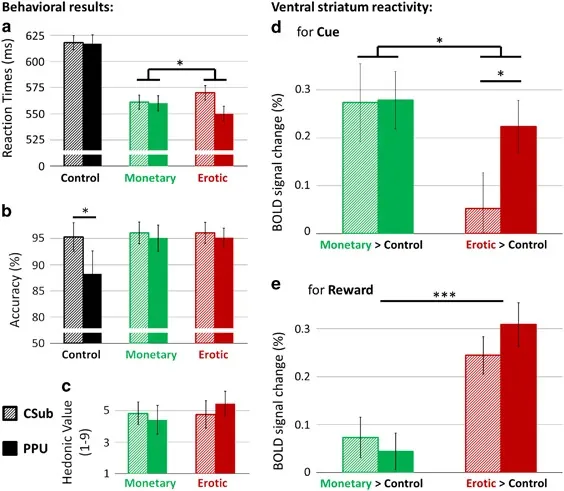
As porn addiction escalates, the "liking" and "wanting" of porn in the brain become imbalanced, and you become extremely sensitive to erotic cues. Let's look at some data and charts to get a direct sense of this. The chart below shows scientists' observations of ordinary people's (represented by the lighter striped bars) and PPU's ("problematic pornography use", represented by the darker bars, which we consider as porn addicts here) reactions to different external stimuli. You can clearly see that PPUs have a much stronger reaction to porn cues than the control group, while in figure e, although porn addicts' reaction to porn rewards is somewhat stronger than the control group, this difference is far less significant than in figure d. This actually points out a fact, the imbalance between "wanting" and "liking", which is that porn addicts are extremely sensitive to porn cues, but not as sensitive and excited about substantial pornographic content.
When you know how researchers provided porn cues, you'll be even more surprised. As you can see from the image below, the so-called porn cue is just a stick figure wearing a bikini. Yet even this stick figure can make addicts' dopamine systems in the brain abnormally active, producing a strong "wanting".
Experimental procedure for porn addiction research: Comparison of monetary and erotic stimuli
This is the worst thing about porn addiction. You desperately want to find pornographic content, but once you find it, you can't feel pleasure that matches your desire. As addiction symptoms further deepen, it evolves into feeling miserable, anxious, and craving when you can't get it, but unable to enjoy or even despising yourself when you do get it.
Next, let's delve deeper into the brain to see what changes have occurred in porn addicts' brains that lead to the imbalance between "wanting" and "liking", and what chemical substances cause the brain to become increasingly sensitive to porn cues. The whole process can actually be divided into the following three steps.
3. Porn overstimulates the brain, leading to excessive dopamine release and frantic seeking
Humans naturally like erotic content; this is a rule written in our genes. Without this rule, the human race couldn't thrive. But due to modern society, all kinds of erotic information are readily available, leading to the most serious problem: "overstimulation". In agricultural times, most people were monogamous, and obtaining sexual resources required great effort for most people. Now, regardless of what race or age you prefer, whatever special preferences you have, you can easily obtain thousands or even millions of times more sexual stimulation than before with just a few clicks and searches. This leads to a problem: with external overstimulation, the dopamine in your brain also secretes excessively.
At the same time, with the massive secretion of dopamine, the brain's sensitivity to glutamate also increases. Glutamate can enhance the brain's sensitivity to cues related to porn addiction. The principle is that glutamate stimulates the number and morphology of dendritic spines in brain neurons, thereby strengthening the connections between neurons. As a result, you become very sensitive to porn addiction cues that trigger massive dopamine secretion. This series of operations, if in ancient times, would actually be beneficial for survival. For example, if you follow the smell of roasted meat and indeed find roasted meat, the brain making you very sensitive to the smell of roasted meat helps you survive, so that next time you can find roasted meat faster. But the problem still lies in "overstimulation" - you no longer need to make much effort to easily obtain enormous pleasure. So your ancient brain can't handle this situation and various malfunctions occur.
When dopamine is excessively secreted, the human brain will initiate an inhibition program. Just as you feel hungry when you're starving, prompting you to eat, your body also provides a feeling of fullness after you've eaten to prevent you from eating endlessly. When you secrete too much dopamine and super "want" something, dynorphin will be massively secreted to suppress the dopamine system and increase tolerance to dopamine, preventing you from endlessly "wanting". However, dynorphin is also related to negative emotions, which to some extent can lead to your anxiety. So if you secrete too much dynorphin, it might lead to another problem: "anhedonia".
Finally, under various brain chemical reactions, accompanied by the arrival of a few seconds of sexual climax, substances responsible for "liking" such as endorphins and serotonin are massively secreted. You'll feel satisfied, happy, and joyful. At this time, you'll briefly enter a true sage time. You'll feel that porn no longer attracts you, you no longer have any desires, and dopamine is no longer released.
But this isn't over. You'll start the next browsing session in a short time because countless new and stimulating content is waiting for you to browse. So you satisfy yourself again and again. Even if you already feel tired and can no longer obtain more pleasure, you still can't stop. You're wrapped up in dopamine, constantly producing various "wants". This state is also called the Coolidge effect.
This is the first stage of porn addiction. You still have strong autonomy, and your brain hasn't encountered any problems. If you're willing, you can choose to stop. But due to external stimuli and your natural pursuit of pleasure, most people won't stop. Instead, they follow their body's desires, frantically watching porn, subjecting their brains to stimulation they shouldn't endure. This also lays the groundwork for porn addiction.
4. From voluntary behavior to compulsive behavior
After the dopamine stimulation disappears, the extended amygdala area in the brain will be activated. This area is mainly responsible for emotions such as anxiety and fear. The resulting negative emotional state leads to the activation of the brain's stress system and the dysregulation of the anti-stress system, while also reducing sensitivity to rewards, meaning your tolerance increases. So you'll watch porn again after a period of time. The reason is that when you don't watch, you become restless and start to feel painful. At this point, your behavior is no longer driven by positive feedback, but gradually becomes driven by negative feedback. You're no longer pursuing pleasure, but gradually escaping pain. Your autonomy decreases, while compulsiveness increases. In other words, the degree of your porn addiction is slowly deepening.
Throughout this process, a transcription factor in the brain called DeltaFosB enhances non-voluntary behavior. This factor has long been considered the switch for addiction. It suppresses dynorphin and increases sensitivity to rewards and reward cues. This molecule has a very special point: although its concentration in the body can't increase as rapidly as dopamine, once it increases, it will maintain for weeks or months.
Do you know what this means? Even if you only watched porn once, your brain will become increasingly sensitive to cues related to porn information for months, deepening your porn addiction. In other words, even if you've stopped watching porn, you'll still be affected by it. Then at some point when you're stimulated by porn cues, you'll return to porn's embrace again.
5. Brain changes, loss of self-control
When you're addicted to porn, your rationality will gradually be consumed, and you'll lose self-control
There's one more thing you should know. Dopamine not only controls humans' natural cravings for food and sex, but also participates in plan formulation and decision-making, affecting cognitive and emotional inhibition functions. For example, when you decide to execute a 30-day fitness plan to lose 5 pounds, dopamine is involved in the execution process, making you "want" the goal of "losing 5 pounds". At this point, your "wanting" is essentially the same as the "wanting" in porn addiction, both driven by your own desires. However, if you continuously watch erotic content, the strong dopamine stimulation will also affect the neuroplasticity of the prefrontal cortex, reducing the volume of gray matter in the brain. Your emotions will become increasingly irritable, you'll have difficulty controlling your behavior, and you'll no longer be able to make good decisions. At the same time, because you've become accustomed to massive dopamine stimulation, and other things don't give you as much stimulation as porn, you'll gradually lose desire for other things. Your hobbies will gradually be abandoned. You'll no longer have much "wanting" for things other than porn, and your emotions will often be in a state of boredom, depression, anxiety, and rage.
At this point, you're completely addicted to porn. Your autonomy disappears, completely turning into compulsive behavior. Your brain neurons become extremely sensitive to porn cues but gradually can no longer derive pleasure from them. Your brain is destroyed, cognitive abilities decline, emotional control ability weakens, and you're unable to execute any decisions involving delayed gratification.
All the processes described above are not just for porn addiction, but apply to other addictive behaviors as well, such as alcohol addiction, drug addiction, gambling addiction, gaming addiction, etc., because these addictive processes all share the same brain mechanism. You'll also discover something: the secretion of various hormones in the brain may initially be for better human survival, so whenever one substance is secreted excessively, another substance will inhibit it, seeking balance. But when the balance is broken (which happens frequently in modern society), you'll experience various problems. A series of negative events can lead to depression, while a series of positive events can lead to addiction. To maintain mental and physical health, you need to maintain various balances - neither always feeling sad nor being overly hedonistic.
Last updated: November 22, 2024
Author: QuitPorn.AI

Want to learn more?
Get our comprehensive e-book "How to Quit Porn Forever" and unlock unlimited AI consultations by becoming a premium member.
Learn MoreRecommended reading
- How to Quit Porn and Stop Masturbating?
- 6 Benefits of Quitting Porn and Masturbation vs 6 Dangers of Continued Use
- Porn Addiction Withdrawal Symptoms: 7 Key Symptomsand Recovery Guide
- How Long Does It Take to Recover From Porn Addiction?
- How to Quit Porn Without Willpower?
- How to Quit Porn for Good: A Permanent Solution to Break Free Forever
- How to Control the Urge to Masturbate: A Three-Stage Approach
- Does Porn Cause Anxiety? Yes, And Here's The Scientific Proof [2024]
- Why Is Porn Addictive?
- Female Porn Addiction
- How to Masturbate Without Porn